
By Carol Peters October 11, 2024
Credit card processing is an essential aspect of running a successful business today. Whether you’re a small business owner, retailer, or eCommerce entrepreneur, understanding how credit card processing works can help streamline transactions, reduce fees, and improve customer satisfaction.
This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about credit card processing—from its basic concepts to the technology behind it, security measures, fees, and more.
What is Credit Card Processing?
Credit card processing refers to the steps involved in completing a transaction when a customer uses a credit card to pay for goods or services. This process ensures that the transaction is authorized, the funds are transferred from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s account, and the payment is successfully completed. The system involves various players and technologies working together to ensure a smooth, secure, and reliable payment experience.
How Does Credit Card Processing Work?
Credit card processing consists of several steps that occur in just a few seconds. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Authorization: The cardholder presents their credit card (physically or digitally), and the merchant submits the transaction for approval. The issuing bank verifies the cardholder’s information and checks if sufficient funds or credit is available.
- Authentication: Once the issuing bank verifies the transaction, it approves or declines the payment. If approved, the transaction proceeds to the next step.
- Clearing: After the transaction is authorized, the payment processor facilitates the transfer of data to the acquiring bank, ensuring everything is in order.
- Settlement: The funds are transferred from the issuing bank (the cardholder’s bank) to the acquiring bank (the merchant’s bank), completing the transaction.
These four key steps happen within seconds, thanks to advanced payment technology.
Key Players in Credit Card Processing
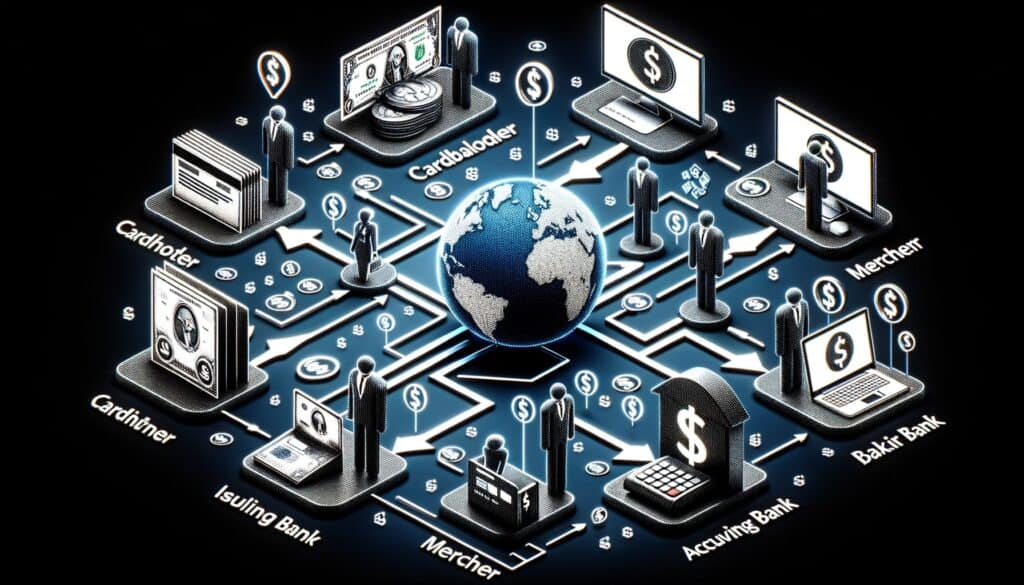
Several parties are involved in the credit card processing ecosystem. Understanding their roles helps businesses navigate and optimize the payment process:
Merchant
The business that accepts credit cards as a form of payment. The merchant initiates the transaction by sending the payment request through the payment processor.
Cardholder
The customer who makes the purchase using a credit card issued by a financial institution (the issuing bank). The cardholder provides the payment credentials necessary to complete the transaction.
Issuing Bank
The bank or financial institution that provides the cardholder with a credit card. The issuing bank authorizes or declines the transaction based on the cardholder’s account balance and credit limit.
Acquiring Bank
The merchant’s bank, also known as the acquiring bank, receives the payment on behalf of the merchant. It facilitates the transfer of funds from the issuing bank to the merchant’s account.
Payment Processor
The intermediary between the merchant, acquiring bank, and issuing bank. The payment processor handles the communication between all parties involved and ensures the transaction is secure and completed.
Types of Credit Card Processing
There are different methods of processing credit card payments, depending on the type of business and how transactions are carried out.
In-Store Credit Card Processing

This type of processing occurs when a customer makes a purchase in a physical store using a credit card. The merchant uses a credit card terminal or Point of Sale (POS) system to process the payment by swiping, dipping (for EMV chips), or tapping (contactless).
Online Credit Card Processing
Online credit card processing is for eCommerce transactions. Customers enter their card information through a website’s payment gateway, and the payment is processed electronically without a physical card present. Online processing requires added security measures like encryption and PCI compliance.
Mobile Credit Card Processing

Mobile processing allows businesses to accept payments through smartphones or tablets using mobile card readers or apps. This is ideal for on-the-go businesses like food trucks, markets, or services that operate outside traditional retail locations.
Credit Card Processing Fees Explained
One of the most significant considerations for businesses is the cost of credit card processing. These fees can vary based on the provider, the type of transaction, and other factors. Below are the common types of fees associated with credit card processing:
- Interchange Fees: Fees paid by the acquiring bank to the issuing bank for processing credit card transactions. They vary based on card type and transaction amount.
- Assessment Fees: Charged by card networks (Visa, MasterCard, etc.) for facilitating transactions.
- Processor Fees: Fees charged by the payment processor for handling the transaction. These may include monthly service fees or per-transaction fees.
- Gateway Fees: For online businesses, a payment gateway is necessary to process payments securely. Payment gateways often charge a monthly fee or per-transaction cost.
Understanding these fees can help businesses choose the most cost-effective credit card processing provider.
Choosing the Right Credit Card Processor
Finding the right credit card processor can significantly impact your business’s operations and bottom line. Here are key factors to consider:
Features to Look For
- Low Fees: Look for processors with transparent fee structures to avoid unexpected costs.
- Security: Choose processors that are PCI-compliant and offer encryption and tokenization.
- Integration: Ensure the processor integrates seamlessly with your existing POS systems or eCommerce platform.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer service is critical in case of any issues or downtime.
- Flexibility: Opt for processors that offer flexibility in terms of payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and digital wallets.
How to Compare Processors
- Pricing: Compare monthly fees, transaction fees, and hidden charges.
- Contract Terms: Check for early termination fees or long-term commitments.
- Service Reviews: Research user reviews and ratings to get an idea of the processor’s reliability.
- Compatibility: Ensure the processor works well with your industry and business model.
Security in Credit Card Processing
With the increase in online transactions and digital payments, security in credit card processing has become more critical than ever. Businesses must ensure they are using secure payment systems to protect both themselves and their customers from fraud.
PCI Compliance
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies accepting credit card payments maintain a secure environment. Being PCI-compliant is a requirement for businesses that process credit card payments.
Encryption
Encryption ensures that sensitive cardholder data is converted into a secure code during transactions, making it unreadable to unauthorized users.
Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive credit card information with unique identification symbols (tokens), which cannot be used outside the transaction process, thus enhancing security.
Benefits of Credit Card Processing for Businesses
There are numerous benefits of accepting credit cards for your business:
- Increased Sales: Offering credit card payments can increase your customer base as it provides a convenient payment method.
- Customer Convenience: Customers expect businesses to accept credit cards, especially with the rise of contactless payments.
- Faster Transactions: Credit card processing speeds up checkout times compared to manual cash handling.
- Reduced Cash Handling: Dealing with less cash minimizes risks of theft or loss.
- Enhanced Record Keeping: Credit card transactions are automatically recorded, improving bookkeeping and financial tracking.
- Improved Cash Flow: Credit card transactions typically settle within a few days, ensuring faster access to funds.
Common Credit Card Processing Terms to Know
Here are some key terms you should be familiar with in the world of credit card processing:
- Merchant Account: A special type of bank account that allows businesses to accept credit card payments.
- Chargeback: A transaction reversal initiated by the cardholder, usually due to fraud or a dispute over a purchase.
- CVV: Card Verification Value, a security code on the back of credit cards used to prevent fraud.
- EMV: Europay, MasterCard, and Visa—a standard for cards equipped with computer chips that provide enhanced security.
- NFC: Near Field Communication, a technology that enables contactless payments by tapping a card or phone.
- Batch Processing: The process of grouping multiple credit card transactions for processing at the end of the day.
FAQs
Q.1: What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
A payment gateway is a software that transmits transaction data from the customer to the payment processor. The payment processor is responsible for communicating with the banks involved and facilitating the transaction.
Q.2: Are there any hidden fees in credit card processing?
Some providers may charge hidden fees, such as monthly service charges or statement fees. Always read the terms and conditions carefully and ask for a transparent fee structure.
Q.3: How long does it take for credit card payments to be deposited into my account?
Typically, credit card payments are deposited into your account within 1-3 business days, depending on your payment processor and bank.
Q.4: How can I lower my credit card processing fees?
To lower fees, negotiate with your payment processor, choose a processor with transparent pricing, and consider alternative pricing models like interchange-plus pricing.
Q.5: What should I do if a transaction is flagged as fraud?
If a transaction is flagged as fraud, immediately notify your payment processor. Ensure that your system is secure and review the flagged transaction for any discrepancies.
Conclusion
Credit card processing is an integral part of modern business operations. From understanding the key players involved to choosing the right provider and ensuring security compliance, mastering credit card processing will improve both your bottom line and your customer experience. With the right knowledge and tools, you can optimize your payment systems and offer convenient, secure, and efficient transactions to your customers.
This guide aims to equip you with all the essential information on credit card processing, helping you make informed decisions to enhance your business’s payment solutions.
